DevOps
Introduction
DevOps is the combination of cultural philosophies, practices, and tools that increases an organization’s ability to deliver applications and services at high velocity: evolving and improving products at a faster pace than organizations using traditional software development and infrastructure management processes. This speed enables organizations to better serve their customers and compete more effectively in the market.
AWS DevOps Real-time Projects Online Training in Hyderabad
Key Takeaways
• AWS CodePipeline is a DevOps service for Continuous Integration, Continuous Delivery and Continuous Deployment of applications hosted on various AWS platforms.
• Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) is an AWS managed service for containerized applications for Docker containers.
• Amazon Fargate is a serverless launch type for Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS).
• For the example application deployed to ECS, an AWS CodePipeline consists of a source code repository such as a GitHub repo, AWS CodeBuild for Build and an AWS ECS (Fargate) service for Staging.
• The benefit of using an AWS CodePipeline for an AWS ECS service is that the ECS service continues to run while a new Docker image is built and deployed.
Docker containers may be deployed using one of the several cloud platforms, Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) being one of them. ECS provides the Fargate launch type, which is a serverless platform with which a container service is run on Docker containers instead of EC2 instances.
Problem
A Docker container deployment may need to be updated or modified due to changes in the Docker image source code or code build. Any modifications in the source code for a Docker image would require that a Docker image be rebuilt and the Docker service be redeployed. Without a mechanism to integrate, build, deliver and deploy source code while an AWS ECS deployment is running, it would involve stopping the ECS service tasks and as a result, incurring downtime for an ECS service. High availability of an ECS service being a priority, stopping tasks to redeploy an application is not a suitable option.
Solution
AWS CodePipeline is a DevOps service for Continuous Integration, Continuous Delivery and Continuous Deployment of applications hosted on the various AWS platforms, including Amazon ECS and Fargate as a deployment platform. An ECS service may be updated or modified without stopping the ECS service tasks. AWS CodePipeline provides high availability of an ECS service in a dynamic environment in which source code changes for a Docker image are common. A CodePipeline consists of three phases: Source code integration, Source code build, and Deployment, as shown in
Figure 1. CodePipeline Phases
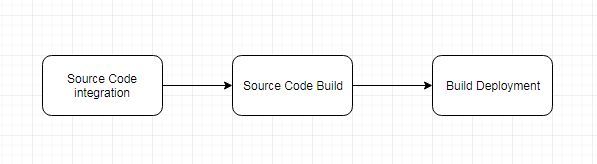
For source code we shall use a Github repository. For source code build we shall use a AWS CodeBuild project. For deployment we shall use an ECS service of launch type Fargate.
Creating and deploying a CodePipeline application to ECS Fargate involves the following procedure:
1. Create an ECS Fargate Task Definition an Service
2. Configure connectivity on Task Subnet/s
3. Create or Configure a S3 Bucket for Output Artifacts from the CodePipeline Build Stage
4. Create a CodePipeline to deploy a Docker platform application (image) on ECS Fargate
5. Modify Input/Output Settings for Stage Artifacts
6. Run the CodePipeline
7. Make source code modifications to re-run CodePipeline
Also Read: How to success in the cloud with these proven DevOps strategy
How to Deploying Docker Containers Using AWS CodePipeline for DevOps
AWS DevOps Real-time Projects Online Training in Hyderabad
Setting the Environment
The only prerequisite is an AWS account. The application deployed by a CodePipeline on ECS Fargate is a Docker application. Any Docker image that has source code repo could be used and we have used Docker image dvohra/node-server. Here is the GitHub source code repository for the Docker image
dvohra/node-server.
Creating a GitHub Code Repository
If a new GitHub source code repository were to be used, it must include a Dockerfile from which to build Docker image. The Dockerfile for the dvohra/node-serverimage is based on the Docker image node:4.6. Dockerfile instructions copy a server.js file, which is used to create a Node server, to the current directory, expose port 8080 for the Node server to listen on, and run a node command on the server.js script. The server.js file creates a Node server and handles an HTTP request/response.
Adding a Build Spec for CodeBuild Project
A build spec is a YAML syntax file with build commands and settings used by a CodeBuild project to run a build. The build spec file must be called “buildspec.yml” and must be copied to the root of the source code repository. A buildspec.yml file consists of key/value pairs to describe the various phases of a build. The build phases are represented with the phases sequence, which is a required mapping in a buildspec.yml. The version is the other required mapping in a buildspec.yml. The buildspec.yml file is listed on the GitHub repo.
Adding an Image Definitions File
For deploying Container based applications such as those deployed to ECS, AWS CodePipeline requires an Image definitions file in JSON format. The Image definitions file is called imagedefinitions.json by default but could be given another name. The image definitions file describes the container application and consists of two attributes: name and imageURI. The name specifies the Docker container name and the container must be running prior to running the CodePipeline. TheimageURI specifies the Docker image to be run in the Docker container. The Docker image would typically be the same as the Docker image already running in an ECS container. The image could be different and the variation would typically be of the image tag.
The imagedefinitions.json used for the Node server application deployed to ECS Fargate is listed on the GitHub.
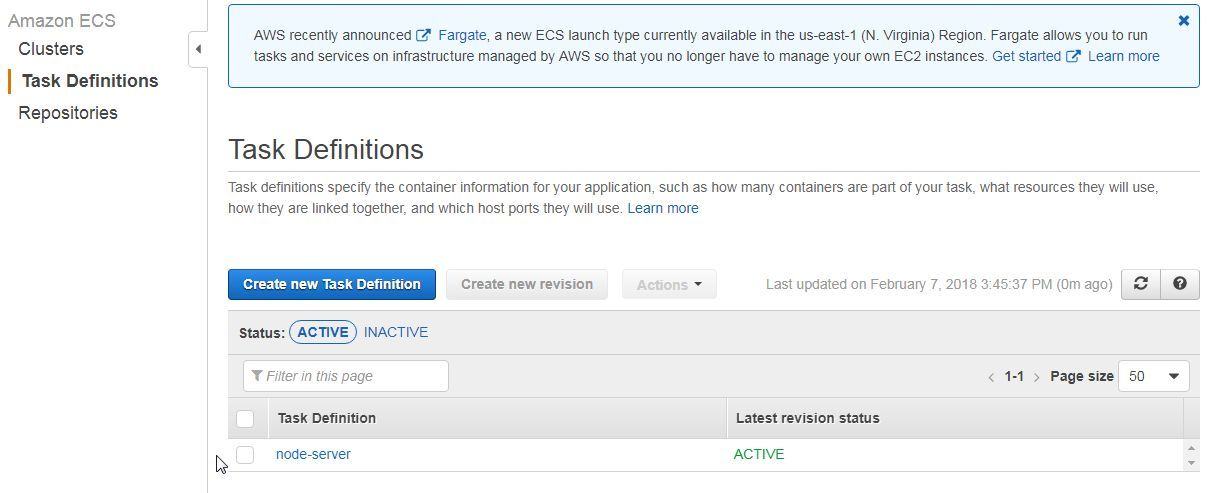
Creating a Task Definition
A task definition in an ECS application describes the container/s in the ECS deployment. In this section, we shall create task definition for a Node Server container to be deployed on ECS Fargate. Open this URL and log in if not already logged in.. Click on Get started to access the ECS Console. Click on Task Definitions in the navigation margin. In the Task Definitions click on Create new Task Definition. In the Create new Task Definition select launch type compatibility as Fargate. Click on Next step. Next, configure task and container definitions. In the Add container dialog specify a Container name (node-server) and specify Image as dvohra/node-server. The task definition is shown in Figure 2
Figure 2. Task Definition
Configuring Connectivity in Task Subnets
Before creating a service we need to configure connectivity to the Internet in the Subnets to be used when configuring the service. The Route Table lists the routes. We need to add a route with a default Internet gateway. Add a route with Destination as 0.0.0.0/0, which is an IP address. Select Target as an internet gateway.
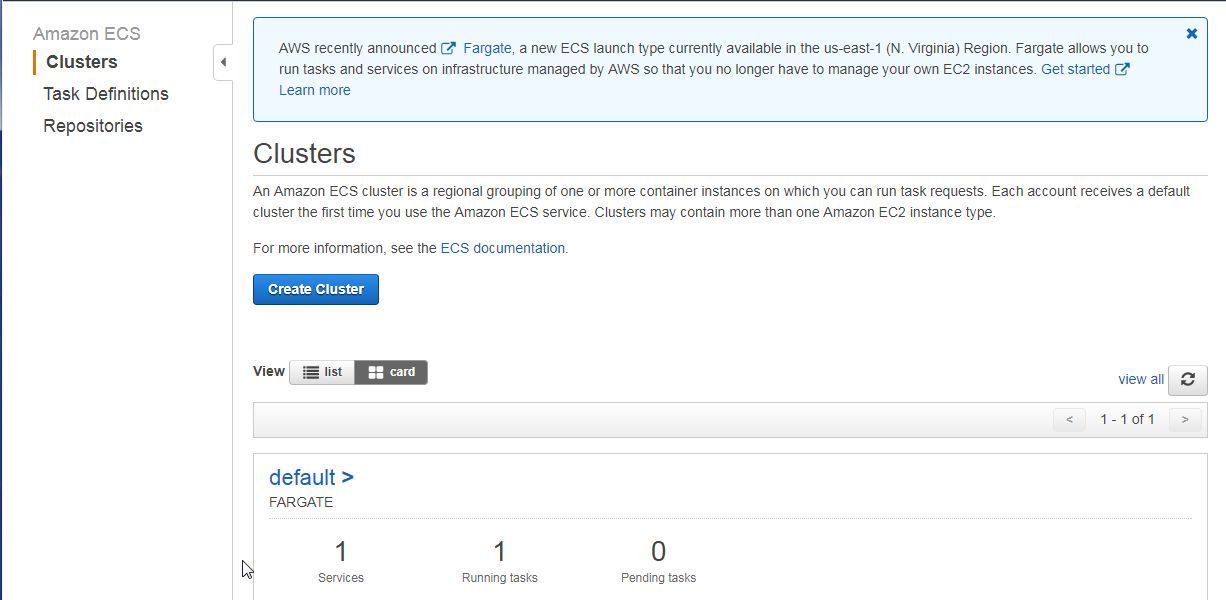
Creating and Testing the Container Service
Next, create an ECS container service in the default cluster as shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3. Cluster with 1 Service
With Fargate launch type an Elastic Network Interface (ENI) is provisioned for each task.
Copy the Public IP of the task, which is the same as the Public IP of the Elastic Network Interface, from either the task Details page Network section or the ENI Console. Open the URL
Recommend to Read
Top 5 Most In-Demand Programming Languages of 2023
Google offers free online machine learning crash course
Best SEO course Training by SEO Expert Best Practice — endtrace
Google Helps Job Seekers to Find Training Programs Nearby
AWS DevOps Job Support from India by 9 yrs. DevOps Expert
Related Articles
Master Your RPA Developer Interview with Real-World Scenario Questions
Preparing for a Senior RPA Developer interview can be challenging, especially when it involves real-world scenarios. To help you stand out, we’ve...
Top 15 RPA Developer Interview Q & A by Senior RPA Dev
Preparing for a Senior RPA Developer Interview? As the demand for automation continues to rise, so does the need for skilled RPA (Robotic Process...
Complete Process of Document Understanding in RPA UiPath
Unlocking the Power of Document Understanding in UiPath In today's fast-paced world, businesses handle a plethora of documents daily. From invoices...
Unlocking the Power of UiPath AI Units: Your Essential Guide
In the realm of automation, UiPath stands out with its innovative AI Units pricing model, designed to empower businesses of all sizes to streamline...
RPA Lifecycle: Ultimate Guide for UiPath Development Success
In the rapidly evolving landscape of Robotic Process Automation (RPA), understanding the RPA UiPath Lifecycle is crucial for both new and seasoned...
Evaluate and Retrieve Data using API and Validate in SAP System using UiPath
Discover the Power of APIs with UiPath: Simplify Your Data Validation in SAP Systems! Are you ready to unlock the full potential of your data?...
