1. Introduce about yourself in brief
Answer: My name is [Your Name], I am a recent graduate with a Bachelor’s degree in Marketing. Throughout my studies and various internships, I have developed a strong passion for digital marketing and its power to reach and engage consumers in innovative ways.
I am eager to apply my knowledge and skills to drive business growth and success through data-driven marketing strategies. I am a quick learner, a team player and possess strong communication and interpersonal skills. I am confident that I can make a positive contribution to your company as a Digital Marketing Fresher.
2. Briefly explain about Digital Marketing?
Answer: Digital Marketing refers to the use of digital channels, such as search engines, social media, email, and websites, to promote a product or service and reach out to a target audience. It encompasses a variety of tactics, such as search engine optimization (SEO), pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, social media marketing, content marketing, email marketing, and more.
The objective of digital marketing is to engage with the target audience, build brand awareness, drive website traffic, and ultimately, generate leads and sales. The beauty of digital marketing is that it allows businesses to track their progress and measure their success in real-time, making it a crucial component of modern marketing strategies.
3. What are the most effective ways to increase traffic to website?
Answer: There are several effective ways to increase organic traffic to a website, some of which include:
Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Optimizing your website for search engines by using relevant keywords, meta tags, and creating high-quality, valuable content can help increase organic search engine traffic.
Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Advertising: Running targeted advertising campaigns on platforms such as Google AdWords or Bing Ads can drive targeted traffic to your website quickly.
Content Marketing: Creating valuable, relevant and engaging content such as blog posts, infographics, and videos can attract and retain a target audience and drive organic traffic to your website.
Social Media Marketing: Promoting your website and content through social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn can help increase referral traffic to your site.
Email Marketing: Building and nurturing a targeted email list, and sending out regular newsletters and promotional emails can drive repeat traffic to your site.
Influencer Marketing: Partnering with influencers in your industry to promote your brand and drive traffic to your website can be an effective strategy.
It is important to note that a combination of these tactics is often the most effective way to drive traffic to a website, as each approach can complement and amplify the results of the others.
4. Explain what is SEO?
Answer: SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, is the process of optimizing a website to improve its ranking on search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo. The goal of SEO is to increase the quantity and quality of organic traffic to a website from search engines.
SEO involves several tactics and techniques such as keyword research, on-page optimization, link building, technical optimization, and more. Keyword research involves identifying the keywords and phrases that your target audience is using to search for products or services like yours.
On-page optimization involves making changes to the content and structure of your website to make it more search engine friendly.
Link building involves acquiring links from other websites that point back to your site, which can help improve your search engine rankings. Technical SEO optimization involves making changes to the backend of your site to improve its crawling and indexing by search engines.
SEO is a long-term strategy, as the results are not immediate. However, it is a cost-effective way to drive targeted and sustainable traffic to a website over time.
5. What are few most used Digital Marketing tools you used?
Answer: As a digital marketing fresher, I have had the opportunity to work with several digital marketing tools, including:
Google Analytics: A powerful tool for tracking website traffic, analyzing user behavior, and measuring the success of marketing campaigns.
Google AdWords: A PPC advertising platform that allows businesses to display ads on Google and its advertising network.
SEMrush: A comprehensive SEO and digital marketing tool that offers keyword research, site audit, and competitor analysis features.
Hootsuite: A social media management tool that allows businesses to schedule, publish and monitor social media posts across multiple platforms from a single dashboard.
Mailchimp: An email marketing tool that helps businesses create and send newsletters, automated emails, and targeted campaigns.
Canva: A graphic design tool that allows businesses to create visually appealing images and graphics for their website and social media platforms.
These are just a few of the most commonly used digital marketing tools. Each tool has its own unique features and functions, and the specific tools used will depend on the goals and needs of a particular marketing campaign.
6. What are key elements involved in On-page optimization?
Answer: On-page optimization refers to the changes made to the content and structure of a website to improve its visibility and ranking on search engines. The key elements involved in on-page optimization include:
Title Tag: The title tag is the text that appears in the search engine results page (SERP) as the clickable link to your website. It should accurately reflect the content of the page and include relevant keywords.
Meta Description: The meta description is a short summary of the page’s content that appears in the SERP. It should be clear, concise, and include relevant keywords.
Header Tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.): Header tags are used to structure the content of a page and indicate the hierarchy of information. H1 tags are used for the main title of the page, while H2, H3, and so on, are used for subheadings.
URL Structure: The URL structure of a page should be short, descriptive, and include relevant keywords.
Content: The content of a page should be high-quality, valuable, and relevant to the target audience. It should also include relevant keywords and synonyms in a natural and readable manner.
Internal Linking: Internal linking refers to the links that connect one page on a website to another. Proper internal linking can help search engines understand the structure and hierarchy of a website, and can also help users navigate the site more easily.
Image Optimization: Image optimization involves compressing images to reduce load time, and using descriptive and relevant file names and alt tags to improve accessibility and visibility to search engines.
These are the main elements involved in on-page optimization. Properly optimizing these elements can improve the visibility and ranking of a website on search engines and provide a better user experience for visitors.
7. Explain what is Sitemap.xml file and how to generate it?
Answer: A sitemap.xml file is a special file that lists all of the pages on a website and helps search engines understand the structure and hierarchy of the site. The sitemap.xml file is a standard format that is recognized by all major search engines and helps them crawl and index the pages of a website more efficiently.
There are several ways to generate a sitemap.xml file, including:
Using a Sitemap Generator Tool: There are several free online sitemap generator tools available that can automatically create a sitemap.xml file for you. Simply enter your website URL and the tool will crawl your site and generate a sitemap.xml file that you can then upload to your server.
Manually Creating a Sitemap.xml File: You can also create a sitemap.xml file manually using a text editor such as Notepad. The file should be written in XML format and follow the standard sitemap.xml protocol.
Using a Plugin or Module: If you’re using a CMS such as WordPress or Drupal, there are plugins and modules available that can automatically generate a sitemap.xml file for you.
Once you have generated your sitemap.xml file, you should submit it to Google Search Console so that it can be used to crawl and index your site.
This can help improve your website’s visibility and ranking on search engines and make it easier for search engines to find and understand the content on your site.
8. Explain what is robots.txt with syntax?
Answer: The robots.txt file is a simple text file that resides on a website’s server and is used to communicate with web crawlers and other automated bots. The purpose of the robots.txt file is to control which pages of a website can and cannot be crawled by search engines and other bots.
The syntax of a robots.txt file is straightforward and uses specific commands to control the behavior of web crawlers. Here is an example of a basic robots.txt file syntax:
User-agent: [bot name]
Disallow: [URL path]
User-agent: This line specifies the name of the bot that the following rules apply to. For example, “User-agent: Googlebot”
would apply to Google’s web crawler.
Disallow: This line specifies the URL path that should not be crawled by the bot. For example, “Disallow: /private” would prevent the bot from crawling the “private” directory on the website.
Here is an example of a complete robots.txt file:
User-agent: Googlebot
User-agent: *
Disallow: /admin
In this example, the first line specifies that Googlebot should not crawl the “private” directory, while the second line specifies that all other bots should not crawl the “admin” directory. The asterisk in “User-agent: *” is a wildcard that applies to all other bots.
It’s important to note that while the robots.txt file is respected by most web crawlers, it is not a guarantee that pages listed in the file will not be crawled. Some bots may ignore the file and crawl the site anyway, so it’s important to keep sensitive information protected through other means such as password protection or access control.
9. Explain what is web crawlers and it types?
Answer: Web crawlers, also known as spiders or robots, are automated programs that browse the internet and collect information about websites. They are used by search engines such as Google, Bing, and Yahoo to index the pages of websites and to update their search databases.
There are two main types of web crawlers:
A. Search engine crawlers: These are the crawlers used by search engines to index the pages of websites and to update their search databases. The goal of search engine crawlers is to collect as much information about a website as possible in order to provide the best possible search results to users.
B. Custom crawlers: These are crawlers created for specific purposes, such as collecting data for market research, monitoring a competitor’s website, or aggregating information from multiple sources. Custom crawlers can be created to perform specific tasks and to collect specific types of information.
Web crawlers work by following links on a website and visiting each page they find. They collect information about each page, such as the title, description, and keywords, and use this information to update their databases.
It’s important to note that web crawlers can put a heavy load on a website’s server, especially if the site is large and has many pages. This is why it’s important for website owners to limit the amount of information that crawlers can access, using methods such as the robots.txt file or metatags.
10. What is mean by Indexing and crawling ?
Answer: Indexing and crawling are two related processes that are essential to how search engines work.
Indexing: Indexing is the process of collecting, parsing, and storing information about web pages in a database. When a search engine’s crawler visits a web page, it collects information about the page, such as its content, title, and meta tags.
This information is then stored in the search engine’s index, which is essentially a giant database of all the pages on the web.
Crawling: Crawling is the process of visiting web pages and following links to other pages in order to gather information.
The crawler visits each page, collects information about the page, and adds it to the search engine’s index. The process of crawling and indexing is repeated on a regular basis to keep the search engine’s database up to date.
Together, indexing and crawling allow search engines to provide relevant search results to users. When a user searches for something, the search engine uses the information in its index to find pages that match the user’s query and to rank them based on relevance and other factors.
The results of the search are then displayed to the user, showing the most relevant pages first.
11. Explain types of redirects in SEO
Answer: Redirects are used in SEO to send users and search engines from one URL to another. There are several types of redirects, each with its own benefits and disadvantages. The most commonly used types of redirects in SEO are:
301 redirect: A 301 redirect is a permanent redirect that tells search engines that a page has been moved to a new URL permanently. This type of redirect is typically used when a website’s URL structure has changed and the old URLs are no longer accessible. A 301 redirect passes on most of the original URL’s ranking power to the new URL, making it the preferred type of redirect for SEO purposes.
302 redirect: A 302 redirect is a temporary redirect that tells search engines that a page has been moved to a new URL temporarily. This type of redirect is typically used for temporary changes to a website’s URL structure, such as for seasonal promotions or temporary updates to the site.
Unlike a 301 redirect, a 302 redirect does not pass on ranking power to the new URL.
307 redirect: A 307 redirect is similar to a 302 redirect, but it is more specific and tells search engines that the move is only temporary. This type of redirect was introduced in HTTP 1.1 and is becoming increasingly common.
Like a 302 redirect, a 307 redirect does not pass on ranking power to the new URL.
Meta refresh: A meta refresh is a redirect that is implemented using HTML code and is typically used on a page-by-page basis.
Meta refreshes are not as commonly used as other types of redirects and can cause problems with search engines, as they can slow down the process of indexing and can be interpreted as a form of cloaking.
It’s important to choose the right type of redirect for each situation in order to minimize any potential negative impacts on a website’s SEO.
In general, a 301 redirect is the best choice for most situations, as it tells search engines that the move is permanent and passes on most of the original URL’s ranking power to the new URL.
12. Can you write syntax for 301 redirect, 302 redirect with examples?
Answer:
Sure, here’s the syntax for 301 and 302 redirects in different programming languages:
- 301 Redirect using .htaccess (Apache Web Server):
Redirect 301 /old-page.html http://www.example.com/new-page.html
- 302 Redirect using .htaccess (Apache Web Server):
Redirect 302 /old-page.html http://www.example.com/new-page.html
- 301 Redirect using PHP:
header(“HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently”);
header(“Location: http://www.example.com/new-page.html”);
exit();
?>
- 302 Redirect using PHP:
header(“HTTP/1.1 302 Found”);
header(“Location: http://www.example.com/new-page.html”);
exit();
- 301 Redirect using JavaScript:
<script type="text/javascript">
window.location.replace(“http://www.example.com/new-page.html”);
</script>
- 302 Redirect using JavaScript:
<script type="text/javascript">
window.location = “http://www.example.com/new-page.html”;
</script>
Note: The examples above assume that the redirect is being implemented on the “old-page.html” URL and redirecting to “http://www.example.com/new-page.html“. You’ll need to replace these URLs with your own, as appropriate.
13. Explain What is schema tag?
Answer:
Schema markup, also known as schema.org or structured data, is a type of metadata that is added to a website’s HTML code to help search engines better understand the content on the page. Schema markup provides information about the type of content on a page, such as the page’s title, description, image, and other elements.
The use of schema markup has become increasingly important in recent years, as it can help improve a website’s visibility in search engine results and can provide users with more detailed and relevant information about a website’s content.
For example, a recipe website that uses schema markup can display rich snippets in the search results that show the recipe name, ingredients, cooking time, and rating.
There are many types of schema markup, including schema markup for articles, local business information, events, products, and more. Schema markup is added to a page using HTML code and is based on a standardized vocabulary provided by schema.org.
To implement schema markup, you can use tools such as Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper or the Schema App markup editor.
Also Read:
How to Perform a Technical SEO Audit for a website?
How to Improve Organic CTR Website – SEO Ranking Tips?
Off-page SEO Optimization Techniques to drive organic traffic
12 SEO Techniques :How to grow Organic Traffic of Website
Top 10 SEO Success Factors to Rank High in SERP
Technical SEO Guide: Crawl, Index, Rank your website quickly
14. What are the regularly used Schema tags for B2b website?
Answer: For a B2B website, some of the most commonly used schema tags are:
Organization schema: This schema provides information about the organization, such as the name, logo, address, and contact information.
LocalBusiness schema: This schema provides information about a local business, including its address, phone number, and hours of operation.
Service schema: This schema provides information about the services offered by the business, including a description, price range, and geographic area served.
Product schema: This schema provides information about a product, including its name, image, description, price, and availability.
Event schema: This schema provides information about an event, including its name, date, time, location, and description.
Review schema: This schema provides information about customer reviews, including the reviewer’s name, review text, and rating.
Offer schema: This schema provides information about a product or service that is being offered for sale, including the price, availability, and terms of the offer.
Breadcrumb schema: This schema provides information about the page’s location within the website’s hierarchy, making it easier for users to navigate the site.
These are just a few examples of the types of schema tags that can be used on a B2B website. The specific schema tags used will depend on the type of content and information being presented on the site.
15. What are the frequently used Schema tags for ecommerce website?
Answer: For an e-commerce website, some of the most commonly used schema tags are:
Product schema: This schema provides information about a product, including its name, image, description, price, and availability.
Offer schema: This schema provides information about a product or service that is being offered for sale, including the price, availability, and terms of the offer.
AggregateOffer schema: This schema provides information about the total number of offers for a product and the lowest price of the offers.
Review schema: This schema provides information about customer reviews, including the reviewer’s name, review text, and rating.
LocalBusiness schema: This schema provides information about a local business, including its address, phone number, and hours of operation.
Organization schema: This schema provides information about the organization, such as the name, logo, address, and contact information.
Breadcrumb schema: This schema provides information about the page’s location within the website’s hierarchy, making it easier for users to navigate the site.
Product category schema: This schema provides information about the category of a product, helping to improve the organization and navigation of an e-commerce site.
These are just a few examples of the types of schema tags that can be used on an e-commerce website. The specific schema tags used will depend on the type of content and information being presented on the site.
16. What is CTR and how to improve Click-through rate?
Answer: CTR (Click-Through Rate) is a metric that measures the number of clicks on a particular link divided by the number of impressions or views of that link. It is expressed as a percentage and provides insight into the effectiveness of an ad or link in driving engagement and conversions.
To improve organic CTR, there are several strategies that can be employed, including:
- Creating compelling and relevant ad headlines and descriptions
- Using attention-grabbing images and videos
- Segmenting your audience to ensure ads are shown to the right people
- A/B testing different ad variations to find the most effective approach
- Utilizing social proof, such as customer reviews and ratings
- Making the call-to-action clear and prominent
- Targeting the right keywords and topics
- Optimizing landing pages for relevance and user experience
Improving CTR requires a combination of factors, including audience targeting, ad relevance, and user experience. By continuously testing and refining your approach, you can improve CTR and drive more conversions for your business.
17. Explain what is keyword in SEO standpoint?
In the context of SEO, a keyword is a word or phrase that is used to describe the content of a webpage or website. The purpose of using keywords is to help search engines understand the content of a page and match it to user search queries.
By including relevant keywords in a webpage’s content, title tags, meta descriptions, and other areas, a website can increase its visibility in search results and attract more organic traffic.
Keywords are an important part of any SEO strategy, as they provide a way for search engines to categorize and rank pages based on the relevancy of the content to user search queries.
It’s important to use keywords effectively by researching which keywords are most relevant to your target audience, optimizing your content around those keywords, and avoiding keyword stuffing, which is the practice of using too many keywords in a page’s content.
By focusing on high-quality content and effective keyword optimization, a website can improve its search engine rankings and attract more qualified traffic to its pages.
18. What are the key areas keywords be used to drive more traffic to a website?
There are several key areas where keywords can be used to drive more traffic to a website:
Page Titles: The title tag is one of the most important elements for on-page SEO, and including relevant keywords in the title can help increase visibility in search results.
Meta Descriptions: The meta description is another important area for including keywords, as it provides a brief summary of the page’s content and can influence click-through rates from search results.
Headings: Headings (H1, H2, H3, etc.) provide structure to a page’s content and can be used to highlight important keywords and topics.
Content: Including relevant keywords in the body of a page’s content can help search engines understand the context and relevancy of the content to user search queries.
URL Structure: The structure of a page’s URL can also be optimized for keywords, by including relevant keywords in the URL string.
Image Alt-Tags: Alt-tags provide a text description of an image and can be used to include relevant keywords for image-based searches.
By optimizing these key areas for keywords, a website can increase its visibility in search results and attract more organic traffic. However, it’s important to balance keyword optimization with high-quality SEO Optimized content and user experience, as search engines will penalize websites that use keywords in an excessive or spammy manner.
19. Explain What is Long-tail keyword and Short-tail Keyword?
Long-tail keywords and short-tail keywords are two types of keywords used in search engine optimization (SEO).
Short-tail keywords are typically one or two words in length and are highly competitive and broad in scope. Examples of short-tail keywords might include “shoes”, “travel”, or “technology”. These keywords are often too broad to drive significant traffic to a website and are often used as starting points for keyword research.
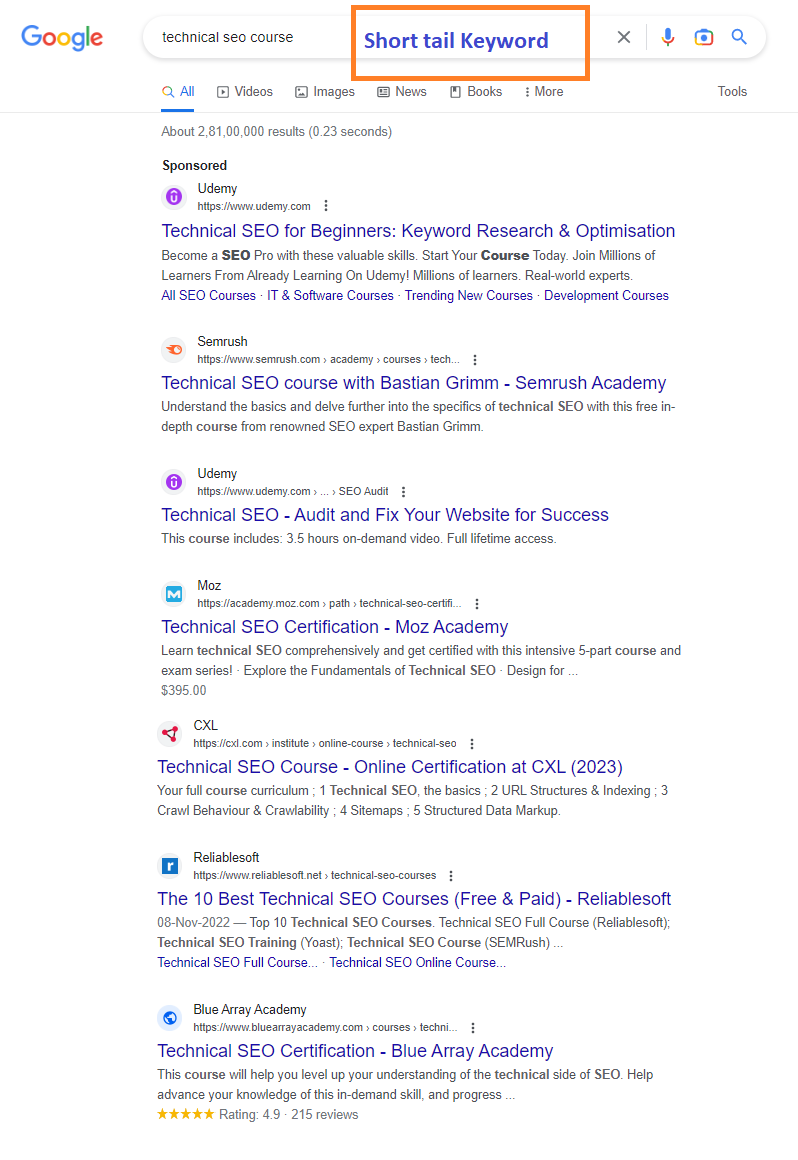
Long-tail keywords, on the other hand, are longer phrases that are more specific and targeted. They typically consist of three or more words and are more likely to drive qualified traffic to a website.
Examples of long-tail keywords might include “best running shoes for flat feet”, “affordable travel destinations in Europe”, or “new technology products for home automation”.
Long-tail keywords are often less competitive than short-tail keywords and provide a more targeted approach to attracting visitors to a website.
 By focusing on long-tail keywords ?, a website can improve its search engine rankings and attract more relevant and qualified traffic to its pages.
By focusing on long-tail keywords ?, a website can improve its search engine rankings and attract more relevant and qualified traffic to its pages.
In general, it’s recommended to use a combination of both short-tail and long-tail keywords in an SEO strategy, as short-tail keywords can help establish a broad presence in search results, while long-tail keywords can help attract more targeted and relevant traffic to a website.
20. Which is you recommend and Why?
I would recommend using a combination of both short-tail and long-tail keywords in your digital marketing and SEO strategies.
Short-tail keywords can help establish a broad presence in search results and give you a general idea of the types of searches that your target audience is making. They can also help you capture high-volume traffic and drive awareness for your brand.
Long-tail keywords, on the other hand, can help you attract more targeted and relevant traffic to your website, as they are more specific and focused. Long-tail keywords can help you connect with people who are further down the sales funnel and are more likely to convert into customers.
In summary, using a combination of both short-tail and long-tail keywords can help you reach a wider audience, establish your brand, and drive more qualified traffic to your website.
Bonus Points:
Comprehensive Guide to On-Page Optimization
In-depth Technical SEO Audit Report manual
Digital Marketing Course Training
As you have now learned about the Technical SEO Interview Q&A, we hope you feel more confident and prepared for your upcoming SEO interview. Remember, continuous learning and practice are key to mastering SEO, and we are here to support you in your journey.
Stay tuned for our next article where we will be sharing even more advanced Technical SEO Interview Q&A to Crack the SEO Interview questions and answers that help you take your SEO skills to the next level. Keep learning and never stop growing!
Related Articles
Are You Looking for Digital Marketing Projects for Best Practice?
You've aced your digital marketing course. Now what? The real challenge begins: gaining practical, hands-on experience. Theory alone won't cut it in...
How to Start a Digital Marketing Projects for Best Practice – Ultimate Guide
Starting a digital marketing project can seem overwhelming, but with a clear, step-by-step guide, you can navigate this journey with ease. Embarking...
Drive Traffic with Organic CTR: SEO Ranking Tips for Website
Introduction: Are you struggling to get your website to rank higher in search results? Are you frustrated by the lack of traffic your website is...
Crack the SEO Interview Q&A | Boost Your Skills & Poise
In our previous article, we covered 20 Technical SEO Interview questions and answers for aspiring SEO professionals. In this article, we will be...
How to do step-by-step SEO Competitor Analysis + Template
Introduction A. Importance of SEO competitor analysis In today's digital landscape, search engine optimization (SEO) has become a critical component...
A Step-by-Step Guide to Adding Yourself to Google Search Card
Introduction Google People Card is a feature that allows users to showcase their personal information and make it easily discoverable by others....
